Phylogeny is used in the science of biology known as taxonomy, as a way of understanding how organisms developed from a common ancestor.
One way of understanding phylogeny is by comparing it to a family tree. The ancestry of your family would, if drawn in the same way as the chart below, resemble the evolution of a species over thousands of years.
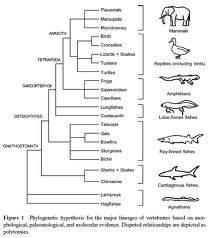
Darwinism and the Tree of Life
Phylogeny became prominent in evolutionary biology during the 1950s, when the long-established method of looking at the development and categorisation of life, the Linnaeus Classification System (Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species), began to be seen as too subjective and open to interpretation. It also did not account for the then-recent discoveries in DNA and its effect in the study of the relationships between species.
Phylogeny was developed as a result. One still needs a firm belief in Darwin's Theory of Evolution, and the idea of a 'tree of life' working backwards to a common cellular ancestor, but with addition of an understanding of DNA and how it can be used to detect similarities between different forms of life.
This film gives you more of the basics of phylogeny: