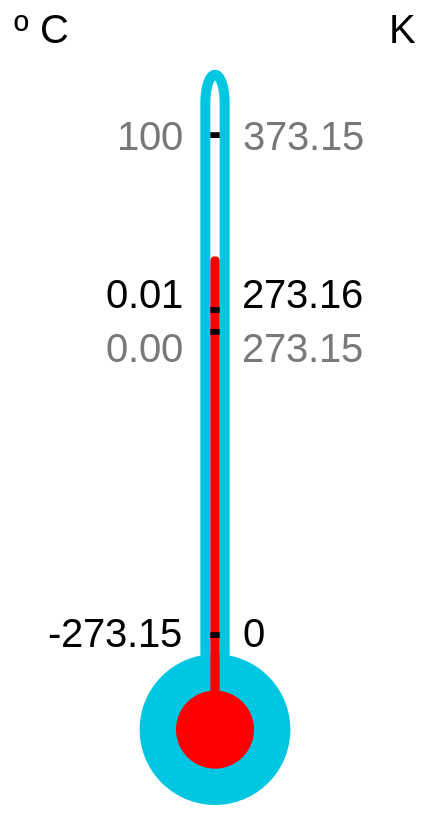
The Kelvin system of temperature measurement takes its base point as absolute zero, which is commonly taken to be -273.15 degrees Celsius, or -459.67 degrees Fahrenheit. Absolute zero is Kelvin is known as 0 degrees K. The scale in Kelvin works it way upward from 0 K.
The Invention of Degrees Kelvin
The Kelvin system was invented in 1848 by William Thomson, 1st Baron of Kelvin, and an engineer at Glasgow University. Also known for his work on the transatlantic telegraph system and the mariner's compass, Thomson also discovered the coldest possible temperature that could be achieved (though he gave it at -273C, rather than -273.15C, at the time) and proposed a new measurement since using this as its base point.
This film explains more about the science of absolute zero: