The tibia, which is sometimes known as the shin or shank bone, is one of the two lower leg bones along with the long and thin fibula which runs parallel to the tibia. It is the larger and the stronger of the two, and is actually the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur (thigh bone).
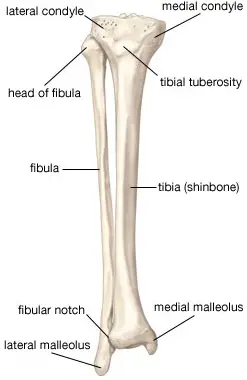
It forms the knee joint with the femur and the ankle joint with the fibula. Some of the most powerful muscles that are essential for the movement of the foot and lower leg are attached to the tibia.
The bone was named after the Greek aulos, which was a flute-like wind instrument.
Injuries
The tibia is the most commonly fractured long bone in the human body. It can also be affected by "shin splints", the term used to describe exercise induced pain in the tibia. Shin pain is often felt during or after strenuous activity, especially running, or sports with lots of quick, sudden movements such as basket ball.