Prokaryotic Organisms
Prokaryotic organisms have their genetic material, the DNA, organized in to structures called nucleoids which are found free in the cytoplasm of the cell. No nucleus is present in prokaryotic organisms. In fact, the name "prokaryotic" means essentially "before nucleus". Prokaryotic organisms also lack other organelles that are present in eukaryotic organisms, such as mitochondria, plastids, and Golgi.
Prokaryotic cells are often considered to be simpler than eukaryotic cells. In some respects, this is true because prokaryotic cells do not have the membrane-bound organelles so characteristic of eukaryotic cells. However, in other respects, prokaryotic cells are very complex. Probably it is best to think of prokaryotic cells as just different from eukaryotic cells.
Two separate Domains of prokaryotic organisms are know to exist. These are the Archaea and Bacteria. These two Domains are probably as different from each other as they are from Eukarya (the Domain of eukaryotic organisms).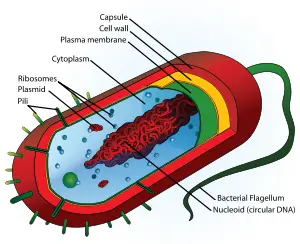
Prokaryotic organisms have their genetic material, the DNA, organized in to structures called nucleoids which are found free in the cytoplasm of the cell. No nucleus is present in prokaryotic organisms. In fact, the name "prokaryotic" means essentially "before nucleus". Prokaryotic organisms also lack other organelles that are present in eukaryotic organisms, such as mitochondria, plastids, and Golgi.
Prokaryotic cells are often considered to be simpler than eukaryotic cells. In some respects, this is true because prokaryotic cells do not have the membrane-bound organelles so characteristic of eukaryotic cells. However, in other respects, prokaryotic cells are very complex. Probably it is best to think of prokaryotic cells as just different from eukaryotic cells.
Two separate Domains of prokaryotic organisms are know to exist. These are the Archaea and Bacteria. These two Domains are probably as different from each other as they are from Eukarya (the Domain of eukaryotic organisms).
