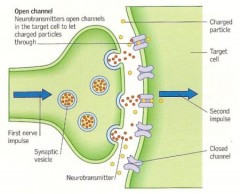
In more detail about the mechanism of transmission...
The nervous system functions by conducting an electrical signal or impulse along the length of the nerve and transmitting it across a junction (called the synaptic cleft) to another nerve or to a muscle fiber. When a nerve impulse reaches the terminus of the nerve, an influx of ions promotes the release of vesicles containing a neurotransmitter such as acetylcholine, allowing this messenger molecule to diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to specific receptors.